If you haven’t read part one of our PPAP series Production Part Approval Process Aims to Improve Communication, you might want to start there.
What are the Elements of the PPAP Package?
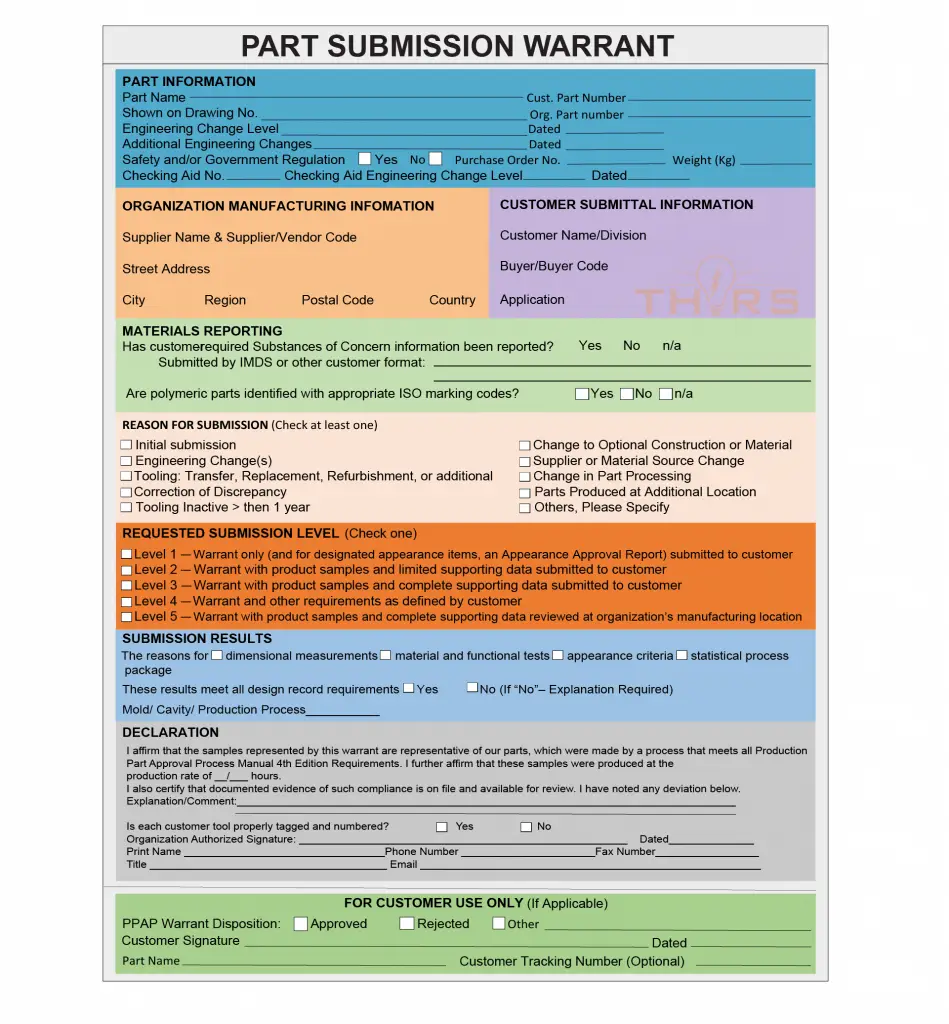
- Part Submission Warrant (PSW): The PSW is the first element of the PPAP package and is an all-inclusive document that provides a summary of the PPAP submission. The supplier should create a separate PSW for each part number or material.
- Design Documents: Design documents refer to the product drawings in the case of production parts and process specifications in the case of bulk materials.
- Design Change Documents: The design change documents are the customer authorization records for approval of any changes made to the product design.
- Customer Engineering Approval: The customer engineering approval is the record of the engineering approval granted by the customer’s design authority.
- Design Failure Mode Effects Analysis (DFMEA): A DFMEA is an element of the PPAP package as systematic documentation to identify and evaluate potential risks in the product design.
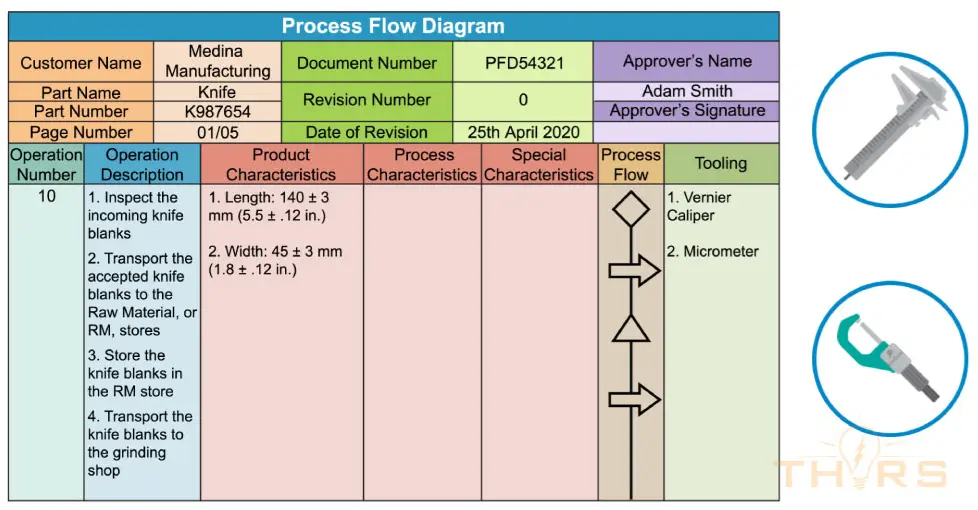
- Process Flow Diagram (PFD): The PFD is a graphical representation of all the operations in a manufacturing process, depicting the production process steps that must be designed to show that it meets the customer’s expectations.
- Process Failure Mode Effects Analysis (PFMEA): The PFMEA is a risk analysis tool designed to identify, evaluate, and control the potential failure modes of a manufacturing process to ensure that the product conforms with the customer’s requirements.
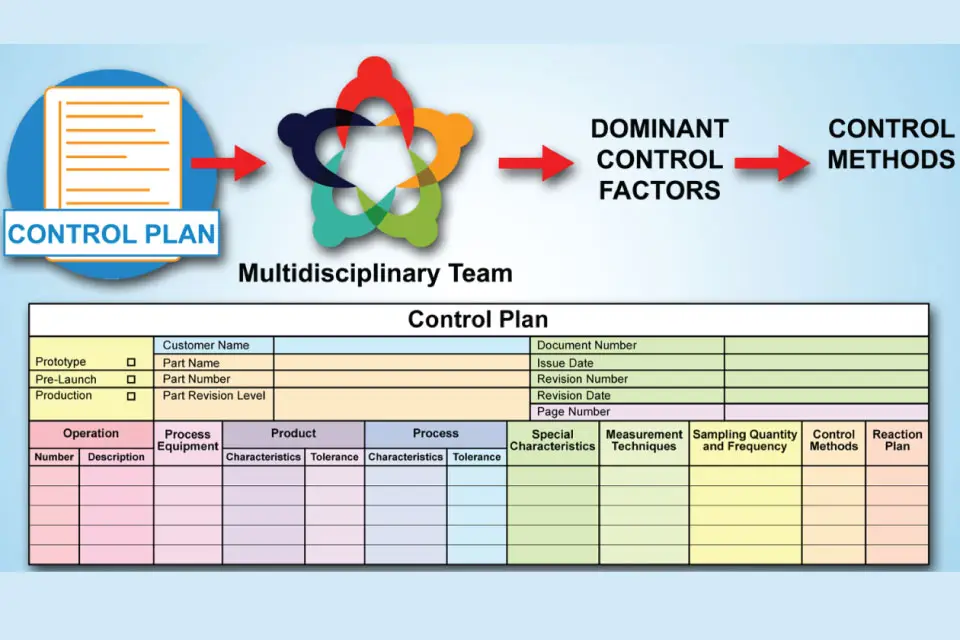
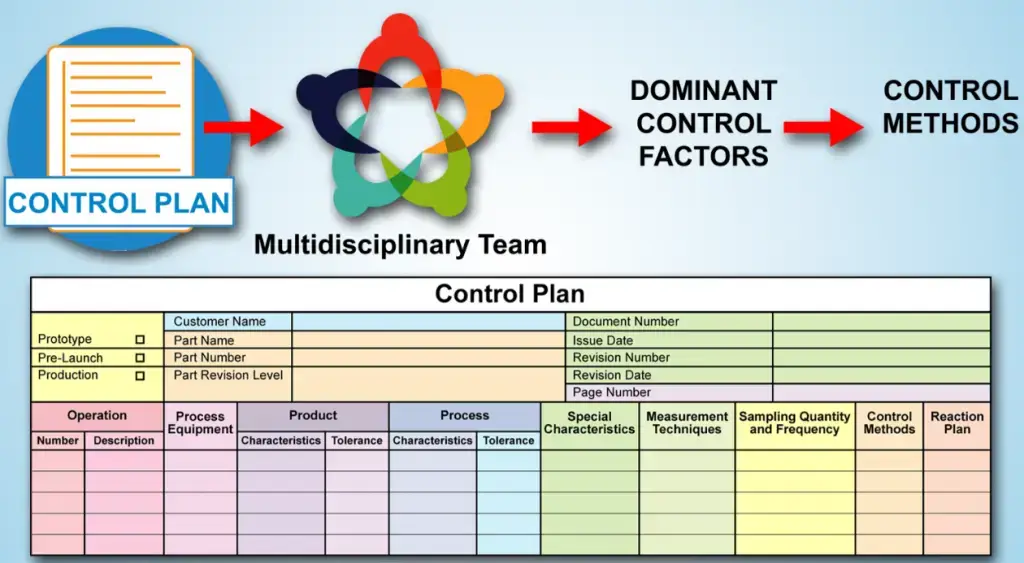
- Control Plan: A control plan is a structured document created to ensure quality and to meet customer expectations in the manufacturing industry. The control plan lists the required control methods for products, processes, and special characteristics at each stage of a manufacturing process to be implemented.
- Measurement System Analysis (MSA) Studies: MSA is a tool to assess the capability of a measuring system used by a manufacturing organization by analyzing the statistical variations present in each type of measuring and test equipment system.
- Dimensional Check Results: Dimensional check results are the evidence for dimensional verification of the product against the design drawing to prove that the products meet the customer requirements.
- Material and Performance Test Results: Material and performance tests are evaluative measures that the supplying organization must perform as specified by the design document and control plan. The parts or products must be tested for their material characteristics, such as physical, chemical, or metallurgical properties. They must also be tested for performance and functionality.
- Initial Process Studies: Initial process studies are quantitative analyses conducted to determine whether the production process is likely to produce the product that can meet the customer requirements. The supplying organization must use appropriate process capability indices to evaluate the initial performance of the manufacturing process as per customer reference manuals on Statistical Process Control (SPC).
- Qualified Laboratory Documents: Qualified laboratory documents are the records of material and performance tests of the product conducted by the supplying organization in qualified internal laboratories or accredited external laboratories.
- Appearance Approval Report: An appearance approval report is a record that demonstrates that the appearance of the final part or product has been inspected and approved by the customer. The customer identifies certain product characteristics as an “appearance item,” such as color, grain, gloss, texture, metallic brilliance, and distinctness of image.
- Sample Product: A sample product is a specimen of the part or material that the supplying organization submits to the customer in the customer-specified quantity for the bulk material, and in the customer-specified number for the production part.
- Master Sample: A master sample is a reference specimen of the part or the material that is retained by the supplying organization.
- Checking Aids: Checking aids are the measurement systems used in the production process, such as inspection fixtures, variable and attribute gauges, models, or templates.
- Records of Customer-Specific Requirements: The customer-specific requirements are a record of all the supplemental requirements linked to a specific clause of the automotive Quality Management System (QMS) standards, such as IATF 16949 or ISO 9001.
- Bulk Material Requirements Checklist: The bulk material requirements checklist is a format to specify all customer-specific requirements applicable to the bulk materials.